...space, Page 7, Experimental confirmation (gravitation)
- Warren Frisina

- Mar 14, 2019
- 2 min read
Updated: May 21, 2019
6.4. Experimental confirmation and predictions, implications
6.4.1. Streaming
It is expected that each large-scale cosmic void within a shell of galactic superclusters is expanding, so that the sum of individual expansions is the observed accelerated universal expansion. On choosing bodies to measure individual void or universal expansion, note should be taken of he position of the body relative to the void -- if on the near side the red shift should be less than on the far side by an "abnormal" amount; that is, if the void is sufficiently close to the observer, the near side may be blue shifted, while the far side is red shifted. This blue shift would be expected with or without the presence of high mass concentrations on the near side shell. This may help explain inconsistencies with red shift readings (streaming) regarding the Hubble flow, apart from the usual local (galactic and galactic cluster scales) fluctuations. Similarly, all red shift readings taken at the intersection of an imaginary plane through the center of any large-scale cosmic void and void shell, the plane being perpendicular to the line of sight, should be consistent with the Hubble flow -- streaming along the line of site apart from local, as mentioned, fluctuations should not be apparent. This proposed added streaming component is distinguished from said local effects by void size; the larger the void the greater the proposed radial component (see Sect. 6.4.5).
6.4.2. Visible matter at void centers
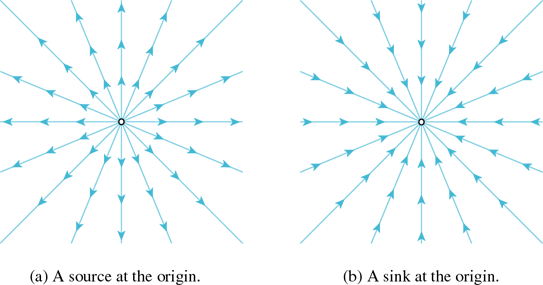
Given a large-scale spherical cosmic void, it is expected that the gravitational field may be expanding radially (in Sect. 3 the spherical mass on the right side of Eq. (2) being negative the radial field would point away from the center, so that (ordinary positive ponderable) visible matter would be more pronounced at the void center than in the remaining volume, less the system of galactic superclusters forming the shell; that is, the radial field should be null about the center, relative to the void in question; globally, however, void centers should accelerate relative to one another (if the visible universe is seen to accelerate as referenced, all constituents should accelerate), indicating the presence of a higher order gravitational field, which would be a composite of individual void fields (barring the cosmological constant). Non-spherical voids may indicate overlapping spheres (see Sect. 6.4.5). In comparison with the gravitational mass-energy of the void, such visible matter is expected to be marginal in quantity and highly localized about the center, as observed (Kuhn, Hopp & Elsassar 19967).





Comments